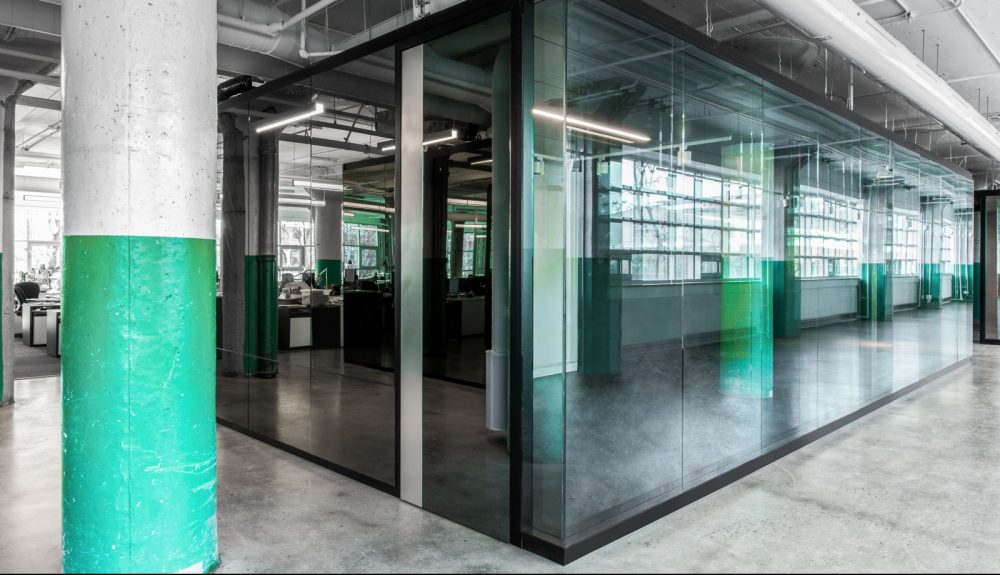
Lemay’s head office, 3500 rue Saint-Jacques
Anonymous submission to MTL Counter-info
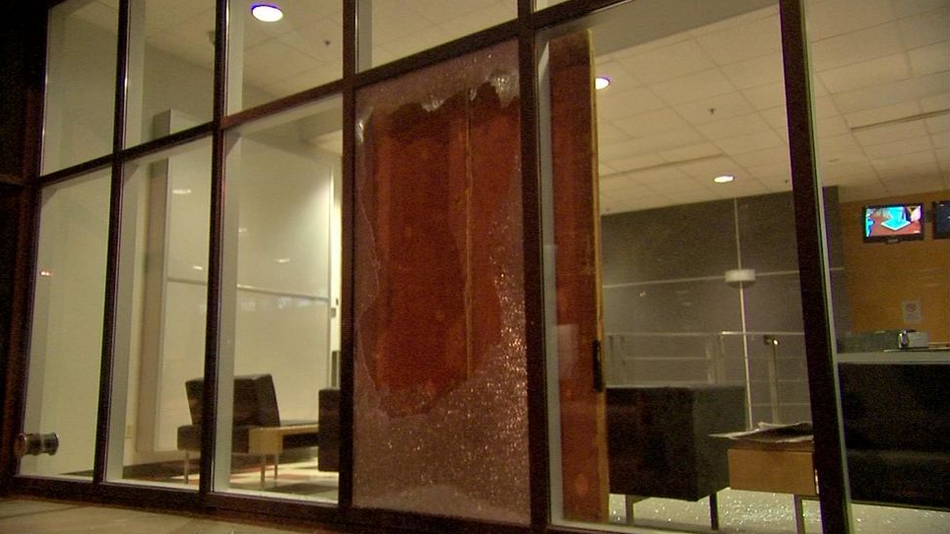
One morning in April 2018, our amateur construction crew released thousands of crickets into the newly built headquarters of the Montreal architecture company Lemay. We pulled a sheet of plywood off the side of the building and funneled the crickets into a recently completed office space. Lemay, along with Quebec-City based company Groupe A, has been awarded a contract to build a new immigration detention centre in Laval, a suburb of Montreal. It is slated to open in 2020. We oppose borders, prisons, and immigration detention centres. We struggle for a world where people are free to stay and free to move; a world without white supremacy, capitalism, colonialism, and patriarchy.
We see the release of these crickets as merely the beginning of a concerted effort to stop the new immigration detention centre from being built. Crickets are known to reproduce quickly and are difficult to exterminate. Their constant noise and quick proliferation through any space they have access to makes them much more than a nuisance to have around. The crickets will multiply inside Lemay’s new headquarters in the gentrifying neighbourhood of St. Henri, even after the wall we deconstructed has been replaced. Meanwhile, we will get even more organized in our resistance to this new immigration detention centre and all that it represents.
The new immigration detention centre in Laval has been proposed as part of a Liberal government “overhaul” of the immigration system. The bulk of the overhaul is focused on infrastructural changes: $122 million of the $138 million overhaul project will be spent on building two new immigration detention facilities (in Laval and in Surrey, BC) and upgrading an already existing detention centre in Toronto. The stated reason for this change is that the current detention centres are not up to international standards. The government claims they also want to move away from detention and towards alternatives to detention.
The new facilities are being pitched as “nicer” prisons. They are supposed to be “non-institutional in design,” and have easy access to outdoor spaces and meeting spaces for family and NGO representatives, but still prioritize state security and keeping people locked up inside. The companies who have been awarded the contracts are known for designing LEED certified court houses and prisons as well as libraries and university spaces. So, it’s hard to imagine that this new prison won’t have an “institutional” feel. Much like the overhaul of the federal women’s prison system in Canada in the 90s and the current attempt by the Ontario provincial government to soften their prison system, this “overhaul” of the immigration detention centre aims to put some pretty curtains on a building that people can’t leave and pretend that it’s okay to lock people up.
The new prison in Laval seems like it will have the same or slightly more capacity to imprison people than the current immigration detention centre (current capacity is between 109 and 144 people, while the new centre would supposedly hold 121 people). This is strange in a context where the numbers of immigrants being detained is down in recent years and the government claims to plan to reduce these detentions even further. It wouldn’t surprise us if they’re just talking more bullshit. As someone said, “if you build them, they will fill them.” A reduction in the number of folks detained seems unlikely.
In fact, let’s talk about that a bit more. As part of the overhaul to the immigration system, Public Safety Minister Ralph Goodale announced the government’s intention to explore “alternatives to incarceration.” In the report that was written about the overhaul, the government said that alternatives to detention included “the ability to report by phone through voice recognition technology to minimize the need to report to the CBSA in person, maximize freedom of movement, facilitate compliance and optimize efficiencies.” Sounds like it’s about making border cops’ jobs easier and saving money.
More commonly known alternatives to immigration detention include electronic bracelets and halfway houses, or a parole-like system run by NGOs willing to act as prison guards. In some ways, these options are better than sitting in a prison. In other ways, these options will act as a carrot, with prison as the stick. In the end, these “alternatives to detention” will reinforce the legitimacy of the detention centre as an option at all (“we gave you a chance to use the phone system and, even though we gave you no option to regularize your status and, in fact, gave you a deportation date instead, you went MIA, so now we have to put you in detention”). Alternatives to detention are more sophisticated forms of controlling migrants that allow the state to seem benevolent, while still deporting and detaining people who don’t submit to the more sophisticated controls.
The strategy of pursuing alternatives to detention would likely lead us further down a road where NGOs collaborate with the government in detaining migrants, in exchange for funding for their staff salaries. In 2017, the government signed a new contract with the Red Cross to monitor conditions in immigration detention centres. However, the Red Cross has technically been monitoring immigration prisons since 1999, this is just the first time they’ve gotten “core funding” for the program from the government. In exchange for $1.14 million over two years, the Red Cross will keep “monitoring” detention centres and telling the government that everything is a-ok; rubber stamping the continued practices of imprisoning migrants. Don’t you just love it when NGOs step in to make government repression look good?
So what do we make of this overhaul in the end? It means more money for more repressive prisons, some money for some slightly less heinous ways of controlling people’s movement, and some money for the Red Cross. In a context where people are walking across the border from the US to flee Trump’s America, a context where most of those people won’t be granted refugee status and they could very well end up in immigration detention, we want to stop this new immigration detention centre from being built. We see this as the perfect time – in fact the only time – to intervene in order to keep this from happening. We mobilize against this new prison, without forgetting that we also want to see the old one closed. We see the prevention of construction on this new prison as just one part of a much larger fight to tear down the others already standing.
In addition to understanding this struggle in the context of a global “migrant crisis,” we understand that this is also happening in a context of a rise of activity in the far right. Storm Alliance, a far right racist anti-immigrant group, has organized a handful of anti-migrant demonstrations at the border, often joined by La Meute, Quebec’s home-grown populist far right group. Influenced by anti-migrant and far-right rhetoric on the internet, Alexandre Bissonnette shot and killed six people in a mosque in Quebec City a year and a half ago. TVA and the Journal de Montreal publish far-right fake news to popularize these sentiments.
With all this in mind, we understand a fight to stop this new detention centre from being built as a fight based in anti-fascism, as part of the fight against white supremacy. We seek to connect our actions to those of other people in our communities, both near and far, who are also fighting white supremacy and the rise of the far right. Even as we fight the liberalism of the current governing party in Canada, we also fight the rise of the far right and their violent visions for the future.
We are inspired, recently, by the campaign to try and stop the deportation of Lucy Granados. We are inspired by the everyday bravery of people living without status and by those who get organized and get together to protect each other and our shared communities. We are inspired by all the people who are standing up against borders, prisons, and other forms of domination. We are inspired to struggle for their freedom to stay and freedom to move, and to call on others to join us.
Lemay is not the only company involved in the design and construction of the prison, and thus not the only possible point of pressure. From the architectural plans of Lemay, to the contributions of Groupe A, to the materials and construction crews, it takes many hands and many parts to build a prison. This is a call for more research, discussion, and action around Lemay’s involvement specifically, but also all the other firms and groups invested in the project. We hope to see other anti-construction crews take action in the future, and we hope that this project can become the target of a sustained campaign, capable of bringing together many people to support an end to prisons and borders.
We hope that the resistance to this prison continues to proliferate, faster and further than thousands of crickets.