Anonymous submission to MTL Counter-info
This series is an attempt to acknowledge and reflect on the history of militant resistance throughout the territories of so-called Canada. While the events we’ll be exploring do not necessarily involve anarchists, we think they’re important – as cultural markers or reference points from which we can be exposed to ideas or tactics. As the old saying goes, we learn from the past to prepare in the present and defend the future.
The following text is on the Computer Riot, which took place in 1969 at Sir George Williams University (present day Concordia University). In an attempt to provide context for the story, we start with a (very) short history of anti-black racism in eastern Canada.
Throughout the first half of the 19th century, tens of thousands of black slaves escaped from American plantations and headed north in search of liberation. Many crossed into Canada, where slavery had been formally abolished in 1834. They settled throughout the eastern provinces – in Ontario, Quebec, and Nova Scotia – forming small, tight-knit communities in urban centres.
These newly landed black migrants were generally met with racist attitudes from white society. Although segregation was never enshrined into Canadian law, they were denied jobs, housing, and access to government services. As the state dreamed its public education system into existence, black children found themselves crammed into segregated and inferior schools. Whites-only establishments were common throughout, with hotels, restaurants, and hospitals refusing service to black patrons.
In response, black communities began to form their own social organizations. In Montreal, numerous community centres were founded to combat social exclusion: the Women’s Coloured Club in 1902, the Union United Congregational Church in 1907, and the Negro Community Centre in 1927. They provided free schooling and healthcare, and distributed food and other resources.
Around the same time, racist groups sought to gain a foothold in the Canadian political sphere by establishing themselves in a number of cities. Montreal saw its own chapter of the Ku Klux Klan, although its power failed to materialize in any significant way. The Klan was briefly popular in Saskachetwan, with a membership of 25,000 that helped James Anderson defeat the Liberal party in the 1929 provincial election.
The black population in Montreal would not see significant growth until federal restrictions on immigration were lifted in the early 1960’s. Between 1961 and 1968, the black population grew from 7,000 to 50,000. This period of influx saw a proliferation of anti-racist, anti-colonial ideas from the US, Africa, and the Caribbean. Black intellectuals drew from the analyses on race and imperialism formulated by members of the Black Power movement and the various movements for independence throughout Africa. They organized conferences throughout the city, echoing the principles of black revolutionary thought: autonomy, self-sufficiency, and defence.
Many young black migrants enrolled at Sir George Williams University (SGW), which offered night classes and a relaxed admissions policy. The university’s heterogeneous population stood in juxtaposition to McGill’s largely white, upper-class student body. Despite its reputation as one of the more inclusive and progressive universities in the country, racism from students and administration was not uncommon at SGW.
In May 1968, six Black Caribbean students submitted a formal complaint against biology professor Perry Anderson. They accused Anderson of discriminating against black students in his class, giving them lower grades for doing the same quality of work as their white counterparts. But after months of inaction, the students became dissatisfied with how their complaint was being handled. They decided to make the issue public, and began organizing sit-ins and distributing leaflets about their situation. In turn, the university established a hearing committee that would vote on the best way to resolve the conflict.
Multiple hearings and assemblies were held throughout January 1969. Professors and other faculty members defended Anderson, while students of colour shared their own experiences of discrimination on campus. Many speakers echoed the words of the Black Panther Party, which had been gaining prominence south of the border. They called for students to be wary of the administration and take matters into their own hands.
On January 29, 200 students walked out of a hearing in protest. They saw the process as a way for the administration to push for Anderson’s innocence and wring their hands of any wrongdoing. After almost 10 months since the original complaint had been lodged, they saw the problem not simply as the prejudices of a particular professor, but the systemic racism found throughout many aspects of the university.
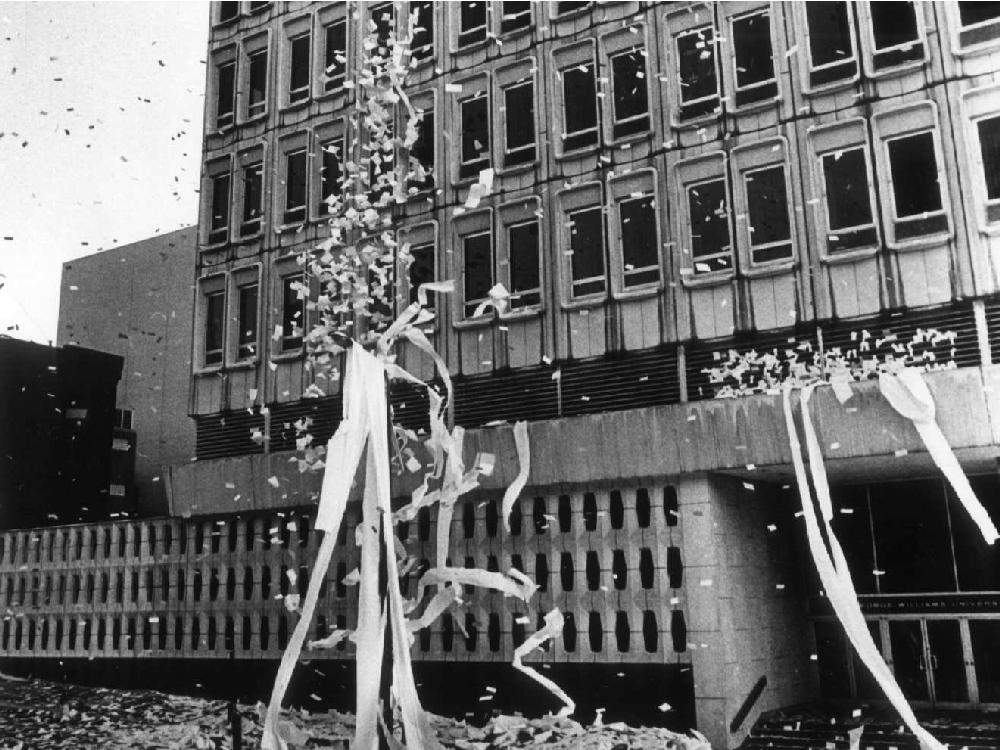
Students set up an occupation of the school’s computer lab on the 9th floor of the Henry F. Hall Building. Nine days later, the occupation spread to the faculty lounge on the 7th floor. On February 10th, the students proposed an end to the protest if the university established another hearing committee and disregarded the classes that had been missed by participants in the occupation. The university also promised to not file charges or pursue police involvement.
With less than a hundred people remaining in the building, riot police began to amass on nearby streets. The university had seemingly gone back on their promise. In response, the students barricaded the stairwells and shut off the elevator system. With cops racing up the stairs, the students chose to use what little leverage they had left, threatening to destroy the millions of dollars of computer equipment if they were not let out safely.
Despite their efforts, the eviction was underway. Students began smashing equipment and throwing thousands of computer cards out of the windows. As police assembled on the 9th floor, a fire broke out on the floor directly underneath. Meanwhile, a white mob that had materialized outside chanted “Let the niggers burn!” Students now attempted to escape by disassembling the barricades, but found that the room’s fire extinguisher and axe were missing. They had been confiscated by cops the day prior.
The protest ended with 97 arrests and approximately $2 million in damages. Anderson, who had been suspended during the crisis, was reinstated on February 12. On June 30, the hearing committee reported “there was nothing in the evidence to substantiate a general charge of racism” and found him not guilty.
This story is a bit different than the “official version.” A quick Google search will turn up dozens of articles about the Computer Riot, almost all of which retell the narrative given by the university. According to them, police were only called to evict the occupation once students had begun barricading the stairwells. This is a classic tactic used to legitimize heavy-handed policing of direct action, claiming that certain control tactics were necessary to pacify a “rowdy” crowd.
Secondly, it’s often claimed that protesters started the fire that caused considerable damage to the building, while the students themselves attest that it was the work of the police. This has most recently been touched upon in the documentary film Ninth Floor.