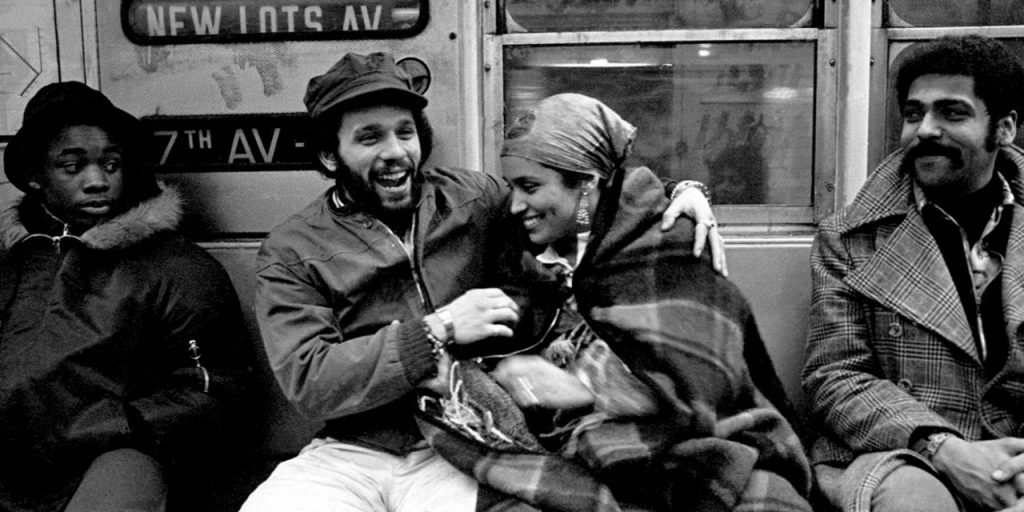
From Archives Révolutionnaires
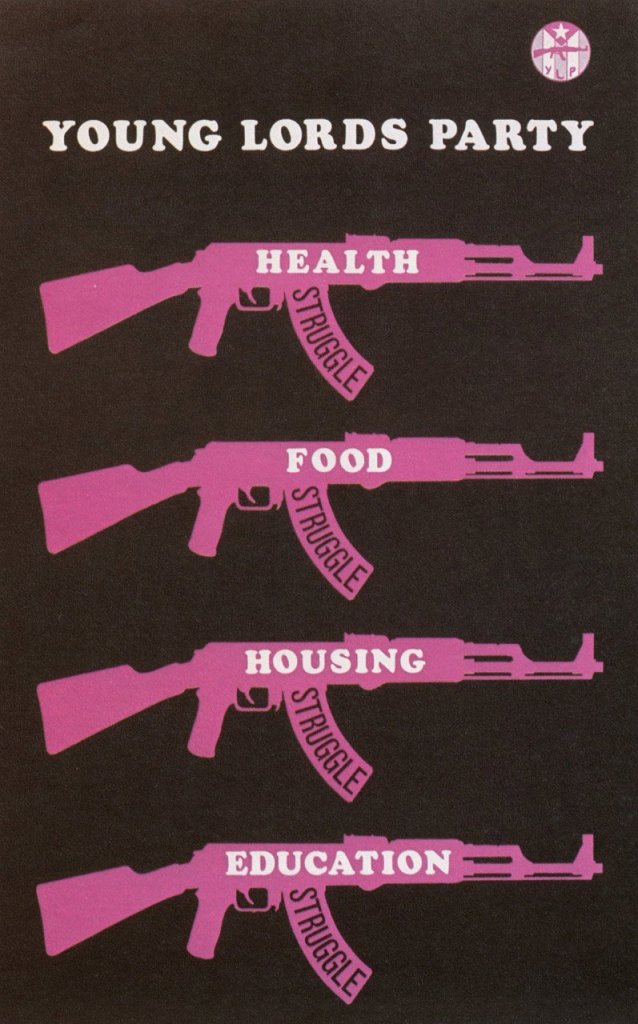
Inspired by the Black Panther Party and other groups of revolutionaries organizing to meet the health and educational needs of their community, members of the Latin American Young Lords Party set up a drug treatment centre in 1970. On November 10, 1970, about 30 activists occupied the then vacant sixth floor of the nurses’ residence building at Lincoln Hospital in the Bronx, New York. He quickly set up checkpoints and erected a barricade; the hospital administration was forced to negotiate and finally give them the space. In partnership with health care workers, addicts and community members, the Young Lords then established The People’s Drug Program, a community-run detoxification program. The following interview, conducted by Molly Porzig, was published on March 15, 2013, in the American magazine The Abolitionnist. Vicente “Panama” Alba, a member of the Young Lords Party and counselor at Lincoln Detox Center during the 1970s, recounts his experience.
/ / /

The Young Lords made seven demands to Lincoln Hospital in July 1970.
What was the Lincoln Detox Center? How did it start and why?
In the late 1960s and early 1970s in New York, we were living through a drug epidemic. In November of 1970, I was 19 years old and had been a heroin addict for five years. I began using heroin when I was 14, which was very common for young men and young women of my generation. Fifteen percent of the population was addicted (communities in the South Bronx, Harlem, the Lower East Side, Bushwick in Brooklyn, including everyone from a newborn baby to an elderly person ready to pass on). The concentration of addiction was on teenagers and people in their early 20s and 30s. Addiction at that time was primarily to heroin.
In the 1960s, the U.S. government engaged in a war in Southeast Asia commonly known as the Vietnam War, but the United States was involved in all of Southeast Asia. There was an airline that was an operation of the CIA transporting heroin from Southeast Asia to the U.S. We see now in Hollywood movies “gangsters” importing heroin, but the bulk of heroin imported to the United States was a United States government operation, targeting poor communities of color, black and Latino communities.
In New York, heroin devastated most of Harlem and the South Bronx. Young people utilized heroin very publicly, sniffing heroin at dance halls or in school bathrooms, which led to shooting up intravenously. This was an epidemic that Black Panther Michael Cetewayo Tabua, one of the New York 21, wrote a pamphlet on called “Capitalism Plus Dope Equals Genocide,” which we used widely. In 1969, the Black Panther Party in New York City was decimated by the indictment of 21 Black Panthers and needed to focus on the trial, becoming inactive in other areas at that time. Because of the relationship the Black Panther Party and the Young Lords had, together we began looking at the heroin epidemic, the general health of our communities and the public health positions of institutions against our communities.
Lincoln Hospital was built in 1839 to receive former slaves migrating from the South. By 1970, it was the only medical facility in the South Bronx. It was a dilapidated brick structure, from the previous century that had never been upgraded. It was known as the “butcher shop of the South Bronx.” In the old Lincoln Hospital (and even today) you walk down the hall and see blood everywhere—blood on the walls, the sheets, the gurneys, your shoes. Doctors were assigned there for internships and learned on Blacks, Puerto Ricans and a very small diminishing white community in the South Bronx.
In early 1970, there was a woman by the name of Carmen Rodriguez who was butchered in the hospital and bled to death on a gurney. Following that death, the Young Lords, with the participation of some Black Panthers, took over Lincoln Hospital for the first time and demanded better health care delivery for people in that community.
“Of course the powers that be did not want us there but could not figure out how to deal with people saying we ain’t going. We’re staying and we’re going to serve our people.”
During the takeover, the Young Lords, Panthers, supporters and translators set up tables where people came to document their experiences of the medical treatment. A major part of the takeover focused on how there were no translators at Lincoln Hospital. South Bronx is a predominantly Puerto Rican community, primarily of Spanish-speaking people newly arrived or second generation who spoke little-to-no English. People would walk in Lincoln Hospital for medical treatment and there was nobody there to understand your ailment or problem. The hospital administration had also been confronted about the lack of services for people with addictions, primarily heroin addiction. The community had told the hospital one of its shortcomings was that you come to the hospital and you get no treatment whatsoever. The hospital administration paid no mind to it.
Months later on November 10, 1970, a group of the Young Lords, a South Bronx anti-drug coalition, and members of the Health Revolutionary Unity Movement (a mass organization of health workers) with the support of the Lincoln Collective took over the Nurses’ Residence building of Lincoln Hospital and established a drug treatment program called The People’s Drug Program, which became known as Lincoln Detox Center.
The police surrounded us and we said we weren’t leaving. By day two, the takeover had spread by word of mouth and we had hundreds of people lined up wanting to get treatment for addiction. About a month later, the administration had to come to terms with the fact that we weren’t leaving. They had been sitting on the proposal of some monies that had been earmarked for treatment that hadn’t been implemented. The money was brought and staff was hired from the very volunteers of the Lincoln Detox program we started. Of course the powers that be did not want us there but could not figure out how to deal with people saying we ain’t going. We’re staying and we’re going to serve our people.
We were very effective in doing so, and kept our program running until 1979.

The Young Lords demonstrate in front of Lincoln Hospital, September 3, 1970.
What was your involvement?
I joined the building of Lincoln Detox from day one. Before that, my primary objective was to go get drugs, until one time Cleo Silvers and I were sitting on a stoop and she pointed some important stuff out to me. She told me to look at the New York City Police patrol car where two officers sat selling heroin. She said, “Look, those are cops. Look who you’re giving your money to!” The climate in our communities at the time is very important. On the one hand we have the drug epidemic, but there was also revolution in the air—change was something that you could breathe, that you could taste, that you could feel, because the movement was very vibrant. Some days before October 30, there had been a massive demonstration called by the Young Lords and I attended the demonstration even though I was still addicted.
Because of the way I felt that day, I told myself I couldn’t continue to be a drug user. I couldn’t be a heroin addict and a revolutionary, and I wanted to be a revolutionary. I made a decision to kick a dope habit. Coincidentally, that day I called Cleo, who told me to go to this place with these people. I met a couple of young brothers from the Puerto Rican Student Union and they escorted me over to Cleo at Lincoln Hospital. It had just been taken over a half-hour before. As I was withdrawing from my addiction, I did not detoxify in Lincoln Detox, but detoxified on my own, cold turkey, a challenge I placed upon myself.
I was recruited out of that experience into the Young Lords Party, maybe a month after the first day of the program. The presence of the Latino movement within the revolutionary movement in the U.S. hadn’t occurred yet in New York. It had occurred in the Southwest with the Brown Berets, but the Latino community in New York was predominantly Puerto Rican. When I joined the Young Lords, I was assigned to Lincoln Detox where I worked as a counselor.
What did the Lincoln Detox Center do? What approaches did it use?
We provided detoxification. We had support from medical doctors providing us with methadone, which we then provided to people in increasing dosages over ten days for people to withdraw, replacing the heroin with methadone and then decreasing it by milligrams every day. After the tenth day you would be physically clean.
This was also right around the time that Richard Nixon opened up relationships with China. A lot came out about Chinese way of life and how health care was provided to the people of China. We heard about acupuncture. We read a magazine article about a situation in Thailand where an acupuncturist used acupuncture to treat someone with respiratory problems and an addiction to opium. We read that the stimulation of the lung point in the ear was the key of the treatment. We went down to Chinatown, got acupuncture needles and began experimenting on one another. We then developed the acupuncture collective within Lincoln Detox.
We also understood that an individual’s addiction wasn’t just a physical problem, but a psychological problem. It was a widespread problem in our community, not because we as a community were psychologically deficient, but because oppression and brutal living conditions drove us to that. There was a book called The Radical Therapist that some of us read.
“The existence of the program was a thorn in the government’s side. We were revolutionaries and radicals doing work, recruiting people to do work the government didn’t want to happen.”


We developed therapy that integrated political education into therapeutic discussions. We held group sessions with overwhelmingly Black and Puerto Rican participants, and engaged in conversations around what it felt like to be Black or Puerto Rican, what it meant for someone who was called a “spic” to not understand what Puerto Rican was. Puerto Rican people are colonial subjects of the United States. You ask a Puerto Rican generally, an unconscious Puerto Rican and they’ll say, “I’m a U.S. citizen.” Well, you are an un-welcomed U.S. citizen, so what does that feel like and mean? The effects of colonialism and the treatment Puerto Ricans receive stateside are not understood because they become internalized. You have to start with what it means. How do you feel about your family’s inability to provide for you? Why do the cops hate you? Why does the school hate you? I went to public school, didn’t know English in 5th grade, and was placed in a class for the “mentally challenged.” There are people who need that support, but I don’t get it. What are the impacts of that kind of treatment by the institutions of society? What happens to a person who lives in those conditions, who gets beaten by police and called a “dirty spic” or who gets denied friendship because the person is white and you’re of color? There is a cumulative impact of this kind of existence and we would discuss it.
How did Lincoln Detox incorporate grassroots organizing into its ongoing work?

When you’re consumed by chasing a bag of drugs, chasing the money to get the bag of drugs, being high, or being in an environment with other people you get high with, it becomes a way of life. When people want alternatives, you have to provide it for them. We did not have the resources to say: Okay, you’re 17, you can benefit from finishing school. Here’s a school with caring teachers, caring counselors and so on to bring people up to speed in education or to direct people to get employment, particularly people who had been out of the work force. Given the natural power of the therapeutic approach, this was all very important that it was voluntary, that it was people’s will to do. If they learned things from our educational program and therapeutic sessions, they wanted to do something about those problems. We would direct them to get involved, to get engaged in campaigns that were going on in the community.
We had people advocating for people in welfare centers, training people on the rights of welfare recipients, and translators who would advocate for people who were Spanish-speakers. We played a part in the founding of a coalition for minority construction workers, because construction work was a good paying job and the industry excluded minorities. Those were a few things we did, in addition to political campaigns. Some people that came through our programs joined the Young Lords, Black Panther Party or the Republic of New Afrika. Some became Muslims and got deeply involved. Some got involved in the campaign to free political prisoners or began building collectives.
We fought everyday—we fought for the right to eat, the right to get paid, the right to be respected, the right not to be fucked with by the cops. We never asked for anything in return.
What were some of the strengths, successes, challenges and weaknesses?
There were strengths and successes throughout, but it wasn’t all glory. There were a lot of challenges and weaknesses. From the first day, November 10, 1970, we had a constant influx of people everyday seeking help. Hundreds and hundreds came—I’m not talking about one or two-dozen people—as the word spread about Lincoln Detox, the opportunity for people to walk in and get effective help from everyday people (not white professionals but their own people) who had a loving heart, developing an understanding of things they needed to articulate. People came from all over New York and Connecticut, Long Island, New Jersey, too. The Lincoln Detox program became so successful and effective that a United Nations delegation visited and gave us recognition for it.
At that point acupuncture became controversial because it was “non-medical” people providing medical care. Laws then were passed about who could do acupuncture, making it so that it could only be done under supervision of a medical doctor who might not have a clue of what acupuncture is about. Those kinds of political struggles—to maintain funding for the program, to keep the program alive, against the local police as well as the hospital police who continuously tried to make their way into the program (Lincoln Detox was a sanctuary where addicts could go and not be afraid of the police)—were big challenges. Then we struggled with the hospital to provide meal expenses for the program. People were coming off the streets, didn’t have anything to eat and needed treatment. We struggled and eventually figured it out.
We also struggled with developing our skills in treatment, acupuncture and detoxing. At the time we started the program, there was a big push to promote methadone maintenance as a treatment modality. Methadone is a scary drug, originally developed by Nazi scientists in order to furnish themselves with opiates. It’s highly addictive and the withdrawal is different from heroin. People slowly developed a protocol for detoxing off methadone. We could detox somebody from heroin in ten days and they’d be fine physically. Methadone was very painful for many months—three or four sometimes.
The existence of the program was a thorn in the government’s side. We were revolutionaries and radicals doing work, recruiting people to do work the government didn’t want to happen.
One morning in 1979, we went to work and the Lincoln Hospital was surrounded by police checking the identification of everybody walking in. They had a list of names and members of the Young Lords, Black Panther Party, and Republic of New Afrika and other people were excluded from entering the facilities, and were to be arrested if they tried to enter. They dismantled Lincoln Detox. One component they were very interested in was the acupuncture, because it was a money mill. Some people today say the Lincoln Detox still exists, but it doesn’t. There’s an acupuncture clinic at Lincoln Hospital but the program was dismantled.
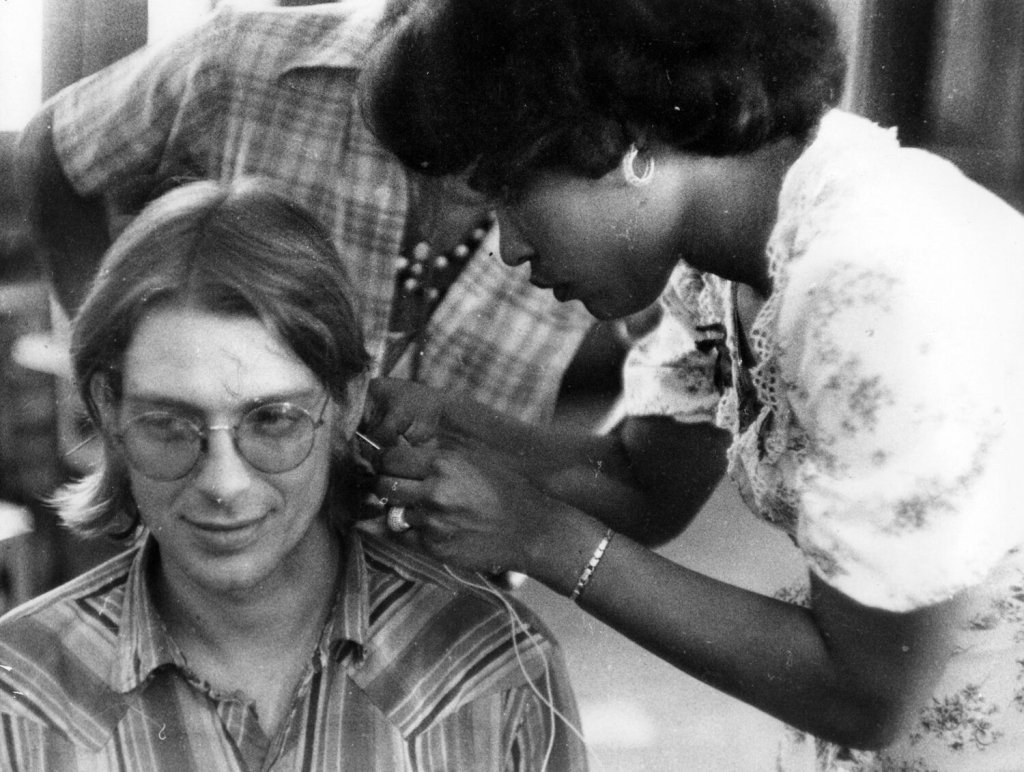

Dr. Richard Taft is receiving acupuncture treatment from a patient intern at Lincoln Detox Center.
Was the collaboration between different groups such as the Young Lords, the Black Panther Party, the Republic of New Afrika and Muslim communities spontaneous, automatic or a more intentional effort in developing the program?
That’s a deep question. There’s the overriding principle of unity and respect and there’s the reality that we were all works in progress. It’s not like you go to sleep one night a junkie and wake up the next morning a revolutionary. There’s a process in growth and change. As products of today’s society, we are not examples of the society we’re building for tomorrow.
Collaboration and solidarity were very important to Lincoln Detox and there were a lot of struggles. We considered the Black Panther Party the vanguard of the revolutionary movement at that time, and there was the reality that the Black Panther Party was disintegrating. There were some people in the Black Panther Party and the Young Lords who were extremely arrogant. We had to struggle against and combat those tendencies. We would always go back to the principle of what is the best interest of the people. The outcome was very positive and we learned so much from each other. In 1973, when the American Indian Movement confronted the FBI at Wounded Knee on Pine Ridge Reservation in South Dakota, there was no question for us. It was automatically our responsibility to support and engage with that. We developed a philosophy, a practice that made it possible for us to do those things.
What lessons were learned that could strengthen work today?
I think that a lot of organizing that takes place today is funded. You don’t hear about many initiatives that are independent efforts. One of the things that Lincoln Detox was very much a part of was support for the Attica brothers during the Attica Prison takeover in September 1971. We did 20-something rallies in 15 days throughout New York City. We didn’t have the Internet or cell phones, or institutions financing copy machines or any of that. We hustled to type fliers, cut and pasted pictures and burned stencils.



Pa’lante (a contraction of Para Adelante, Forward!), is one of the publications of the Young Lords Party, distributed by the New York Chapter.
We built a movement and we looked for ways to make the movement survive without government funding. Nobody could tell us what we were going to do. Today a lot relies on foundation monies, and people focus on the money and don’t engage in campaigns. Even though we forced the government for years to underwrite our work, eventually they had the power and took it out. We didn’t have the power to continue that institution. If we were not in their facility could they have shut us down? I don’t know, but it would have been different.
We need to recognize we can’t have institutions within the institutions. I mean we eventually end up in one way or another in a place where Lincoln Detox ended. We need to think in terms of short range and longer-range efforts. How do you get rid of prisons under imperialism? You have to get rid of imperialism. In the mean time you may take on some struggles that may take on some reforms and that needs to be studied and discussed.
We can look at it from the humanist viewpoint and see that we saved and changed a lot of lives, people who would have been dead from heroin. I’m one of them, one of a lot of people. A lot of people became contributors to progress, but in changing the world the obstacles change too. After heroin came crack. We did not stop the drug scourge in our community.
What are some of the legacies or long-term impacts of the Lincoln Detox center?
Humbly, I don’t think there would be the new Lincoln Hospital without our work. If it weren’t for the struggles that we took on, the new Lincoln Hospital would never have been built, because all political interests had nothing to do with the interests of the people in the community. We had to fight to put the interests of the community at the forefront and demand that hospital be built. When they shut down the old and moved to the new Lincoln Hospital, they made space for every department except Lincoln Detox. The legacy spreads beyond that, too. If you go into any New York City public hospital, you see the Patient’s Bill of Rights on the wall. That came out of the first takeover at Lincoln Hospital. We made it come alive at Lincoln Detox.
What were some of the strengths, successes, challenges and weaknesses?
There were strengths and successes throughout, but it wasn’t all glory. There were a lot of challenges and weaknesses. From the first day, November 10, 1970, we had a constant influx of people everyday seeking help. Hundreds and hundreds came—I’m not talking about one or two-dozen people—as the word spread about Lincoln Detox, the opportunity for people to walk in and get effective help from everyday people (not white professionals but their own people) who had a loving heart, developing an understanding of things they needed to articulate. People came from all over New York and Connecticut, Long Island, New Jersey, too. The Lincoln Detox program became so successful and effective that a United Nations delegation visited and gave us recognition for it.
At that point acupuncture became controversial because it was “non-medical” people providing medical care. Laws then were passed about who could do acupuncture, making it so that it could only be done under supervision of a medical doctor who might not have a clue of what acupuncture is about. Those kinds of political struggles—to maintain funding for the program, to keep the program alive, against the local police as well as the hospital police who continuously tried to make their way into the program (Lincoln Detox was a sanctuary where addicts could go and not be afraid of the police)—were big challenges. Then we struggled with the hospital to provide meal expenses for the program. People were coming off the streets, didn’t have anything to eat and needed treatment. We struggled and eventually figured it out.
We also struggled with developing our skills in treatment, acupuncture and detoxing. At the time we started the program, there was a big push to promote methadone maintenance as a treatment modality. Methadone is a scary drug, originally developed by Nazi scientists in order to furnish themselves with opiates. It’s highly addictive and the withdrawal is different from heroin. People slowly developed a protocol for detoxing off methadone. We could detox somebody from heroin in ten days and they’d be fine physically. Methadone was very painful for many months—three or four sometimes.
The existence of the program was a thorn in the government’s side. We were revolutionaries and radicals doing work, recruiting people to do work the government didn’t want to happen.
One morning in 1979, we went to work and the Lincoln Hospital was surrounded by police checking the identification of everybody walking in. They had a list of names and members of the Young Lords, Black Panther Party, and Republic of New Afrika and other people were excluded from entering the facilities, and were to be arrested if they tried to enter. They dismantled Lincoln Detox. One component they were very interested in was the acupuncture, because it was a money mill. Some people today say the Lincoln Detox still exists, but it doesn’t. There’s an acupuncture clinic at Lincoln Hospital but the program was dismantled.
Was the collaboration between different groups such as the Young Lords, the Black Panther Party, the Republic of New Afrika and Muslim communities spontaneous, automatic or a more intentional effort in developing the program?
That’s a deep question. There’s the overriding principle of unity and respect and there’s the reality that we were all works in progress. It’s not like you go to sleep one night a junkie and wake up the next morning a revolutionary. There’s a process in growth and change. As products of today’s society, we are not examples of the society we’re building for tomorrow.
Collaboration and solidarity were very important to Lincoln Detox and there were a lot of struggles. We considered the Black Panther Party the vanguard of the revolutionary movement at that time, and there was the reality that the Black Panther Party was disintegrating. There were some people in the Black Panther Party and the Young Lords who were extremely arrogant. We had to struggle against and combat those tendencies. We would always go back to the principle of what is the best interest of the people. The outcome was very positive and we learned so much from each other. In 1973, when the American Indian Movement confronted the FBI at Wounded Knee on Pine Ridge Reservation in South Dakota, there was no question for us. It was automatically our responsibility to support and engage with that. We developed a philosophy, a practice that made it possible for us to do those things.
What lessons were learned that could strengthen work today?
I think that a lot of organizing that takes place today is funded. You don’t hear about many initiatives that are independent efforts. One of the things that Lincoln Detox was very much a part of was support for the Attica brothers during the Attica Prison takeover in September 1971. We did 20-something rallies in 15 days throughout New York City. We didn’t have the Internet or cell phones, or institutions financing copy machines or any of that. We hustled to type fliers, cut and pasted pictures and burned stencils.
We built a movement and we looked for ways to make the movement survive without government funding. Nobody could tell us what we were going to do. Today a lot relies on foundation monies, and people focus on the money and don’t engage in campaigns. Even though we forced the government for years to underwrite our work, eventually they had the power and took it out. We didn’t have the power to continue that institution. If we were not in their facility could they have shut us down? I don’t know, but it would have been different.
We need to recognize we can’t have institutions within the institutions. I mean we eventually end up in one way or another in a place where Lincoln Detox ended. We need to think in terms of short range and longer-range efforts. How do you get rid of prisons under imperialism? You have to get rid of imperialism. In the mean time you may take on some struggles that may take on some reforms and that needs to be studied and discussed.
We can look at it from the humanist viewpoint and see that we saved and changed a lot of lives, people who would have been dead from heroin. I’m one of them, one of a lot of people. A lot of people became contributors to progress, but in changing the world the obstacles change too. After heroin came crack. We did not stop the drug scourge in our community.
What are some of the legacies or long-term impacts of the Lincoln Detox center?
Humbly, I don’t think there would be the new Lincoln Hospital without our work. If it weren’t for the struggles that we took on, the new Lincoln Hospital would never have been built, because all political interests had nothing to do with the interests of the people in the community. We had to fight to put the interests of the community at the forefront and demand that hospital be built. When they shut down the old and moved to the new Lincoln Hospital, they made space for every department except Lincoln Detox. The legacy spreads beyond that, too. If you go into any New York City public hospital, you see the Patient’s Bill of Rights on the wall. That came out of the first takeover at Lincoln Hospital. We made it come alive at Lincoln Detox.

Harlem, 1970. Young Lords pose in front of an X-ray truck for tuberculosis detection, a service the organization provided seven days a week.
///
To learn more about the history of the Young Lords, read our article about them. : Young Lords. Histoire des Black Panthers latinos (1969-1976), published by l’Échappée.
[1]